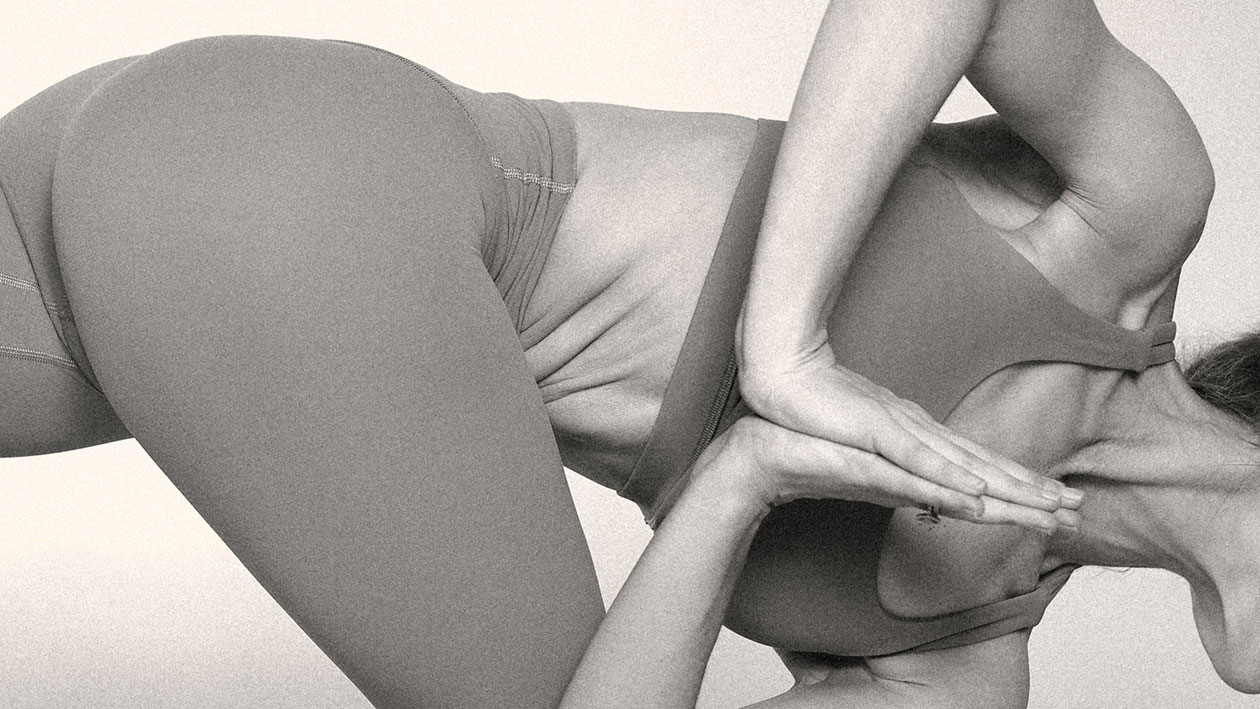
Yes, Pilates is exceptionally effective for stretching and improving flexibility. Research consistently demonstrates that Pilates provides significant flexibility benefits through its unique integration of controlled movements, breathing techniques, and core engagement. Studies show that traditional Pilates with stretching components improves flexibility with a large effect size compared to Pilates routines without stretching elements, making it a superior option for those seeking flexibility improvements and overall health benefits.
Key Benefits of Pilates for Flexibility
Improved Range of Motion
Pilates significantly enhances mobility throughout the body, with particular emphasis on the spine, hips, and shoulders. Research demonstrates measurable improvements in flexibility after just 8-12 weeks of consistent practice, with studies showing significant increases in hamstring flexibility and trunk mobility.
The controlled nature of Pilates movements creates increased muscle length without sacrificing stability, allowing practitioners to safely achieve greater ranges of motion.
Enhanced Postural Alignment
By simultaneously strengthening weak muscles and stretching tight ones, Pilates corrects muscular imbalances that restrict movement and create postural misalignments.
For example, Pilates effectively addresses the forward-head posture and hunched shoulders common among office workers by:
- Stretching tight chest muscles
- Strengthening the upper back
- Improving awareness of proper alignment
- Training the body to maintain better positions
This balanced approach leads to lasting flexibility improvements because it addresses the underlying causes of limited mobility rather than temporarily extending tissues.
Reduced Muscle Tension
The mind-body connection cultivated in Pilates promotes relaxation in chronically tense muscles, allowing them to stretch more effectively. This reduction in muscle tension:
- Decreases the risk of strains and overuse injuries
- Improves overall movement quality
- Creates more sustainable flexibility gains
- Enhances comfort during daily activities
Types of Stretches Involved in Pilates
Dynamic Stretching
In Pilates, the stretching is most often dynamic in nature, with the stretch held for no longer than 2-3 seconds. This dynamic movement is, however, repeated 4-8 times throughout the exercise set [1].
Unlike traditional static stretching, the muscles remain engaged while being lengthened, developing “active flexibility” – the ability to control movement throughout an extended range of motion.
Examples include:
- Roll-up (stretches hamstrings and back while engaging core)
- Spine twist (develops rotational flexibility with control)
- Leg circles (improves hip mobility in multiple planes)
Controlled Movement Stretching
The precise movements characteristic of Pilates create an intelligent approach to stretching that reduces injury risk. Rather than pushing passively into extreme ranges of motion, Pilates emphasises moving with intention and awareness.
This controlled approach:
- Activates the Golgi tendon organs in muscles
- Promotes a relaxation response
- Permits greater lengthening without triggering protective contraction
- Gradually increases range of motion while building strength
Core-Engaged Stretching
Core engagement represents a unique aspect of Pilates stretching that distinguishes it from conventional methods. By maintaining core activation during stretching movements, Pilates creates stability in the centre while mobilising the extremities. In fact, a study found that a Pilates training program was effective in improving abdominal strength and upper spine posture, as well as in stabilising core posture when shoulder flexion movements were performed [2].
Benefits of this integrated approach include:
- Preventing hypermobility risks
- Supporting new ranges of motion with adequate strength
- Enhancing overall movement efficiency
- Improving neuromuscular coordination
How Pilates Improves Flexibility
Physiological Mechanisms
The way Pilates enhances flexibility involves sophisticated processes beyond simple tissue elongation:
- Activation of proprioceptors within muscles and tendons
- Stimulation of Golgi tendon organs, which inhibit muscle contraction
- Mechanical adaptations in muscle tissue
- Gradual rearrangement of collagen fibers
- Increased elastic capacity of connective tissues
Unlike passive stretching, the active engagement in Pilates creates lasting adaptations in both muscle tissue and neural control systems.
There was a statistically significant increase (p = 0.00) in the muscle activation amplitude (RMS) of the femoral and semitendinosus biceps muscles after the Pilates stretching protocol [3].
Core Strength Connection
A strong, stable core provides the foundation from which limbs can safely move through extended ranges of motion. Core engagement benefits flexibility by:
- Creating a supportive cylinder that stabilises the spine and pelvis
- Allowing peripheral joints to move more freely
- Preventing compensatory movements that restrict motion
- Reducing injury risk during stretching
Research demonstrates that the core strengthening aspects of Pilates contribute significantly to its superior outcomes for flexibility compared to isolated stretching approaches.
Postural Improvement
By addressing muscular imbalances and teaching proper skeletal alignment, Pilates removes restrictions to movement caused by poor posture.
For example:
- Exercises that open the chest and strengthen the upper back help correct forward head position
- This postural improvement reduces tension in the neck and shoulders
- Reduced tension allows those areas to achieve greater flexibility
- The precision of alignment ensures stretching occurs in optimal positions
Comparing Pilates to Other Stretching Methods
Pilates vs. Static Stretching
Static stretching typically involves holding a stretched position for 30-60 seconds while remaining relatively passive. In contrast, Pilates offers several advantages:
- Maintains muscle engagement during stretching movements
- Develops strength throughout the new range of motion
- Produces more functional flexibility improvements
- Transfers better to daily activities and athletic performance
Research demonstrates that Pilates participants experience improvements in multiple movement planes, while static stretching groups only improve in limited directions.
Both enhance flexibility but through different approaches:
Yoga:
- Often holds static poses for longer durations
- Emphasises maximum stretch positions
- Incorporates meditation and specific breathing patterns
- May develop end-range flexibility
Pilates:
- Utilises more dynamic movements
- Places greater emphasis on core stabilisation during stretching
- Focuses on controlled mobility rather than maximum stretch
- Develops neuromuscular control throughout ranges of motion
Pilates often provides more directly applicable benefits for individuals with specific flexibility goals related to functional movement patterns.
Pilates vs. Active Isolated Stretching
Active isolated stretching (AIS) shares some similarities with Pilates but differs in key ways:
Similarities:
- Both use controlled movement
- Both involve brief holding periods
- Both engage muscles during stretching
Differences:
- Pilates emphasises whole-body integration
- Pilates develops simultaneous strength during stretching
- Pilates addresses alignment, breathing, and movement quality
- Pilates creates a more multifaceted approach to body development
Who Can Benefit from Pilates for Stretching
Older Adults
Seniors experience particularly significant improvements from Pilates practice:
- The controlled nature makes it exceptionally suitable for older individuals
- Reduces concerns about injury risk compared to aggressive stretching
- Precise movement and proper alignment help seniors improve mobility safely
- Simultaneously addresses age-related balance and strength concerns
Athletes and Active Individuals
Pilates helps athletes develop specific types of flexibility that support their primary activities:
- Core control during stretching helps maintain stability
- Allows access to greater ranges of motion with reduced injury risk
- Develops the combination of mobility and stability needed for optimal performance
- Addresses sport-specific imbalances that can restrict movement
Rehabilitation and Chronic Conditions
Individuals recovering from injuries or managing chronic conditions benefit from Pilates’ approach:
- Progressive nature creates a safe environment for rebuilding range of motion
- Gentle yet effective movements avoid exacerbating symptoms
- Adaptable methodology accommodates particular limitations
- Provides effective stretching benefits with individualized modifications
Pilates offers a sophisticated and effective approach to stretching that goes beyond simply elongating muscles. Its unique methodology – combining dynamic movement, core engagement, proper alignment, and breath awareness – creates lasting improvements in range of motion that translate effectively to daily activities and athletic performance.
For individuals seeking to improve flexibility, Pilates represents an excellent choice that accommodates diverse ages, fitness levels, and specific needs. The controlled nature of Pilates stretching creates a safe yet effective environment for developing flexibility, with consistent practice yielding meaningful improvements in range of motion throughout the body. Get started on your Pilates journey today, reach out to the team at SOHL Studio who will be happy to assist you.
Sources: